- Fukuoka Prefecture
- Oita Prefecture
- Hiroshima Prefecture
- Ehime Prefecture
- Gifu prefecture
- Aichi prefecture
- Kyoto Prefecture
- Yamaguchi prefecture
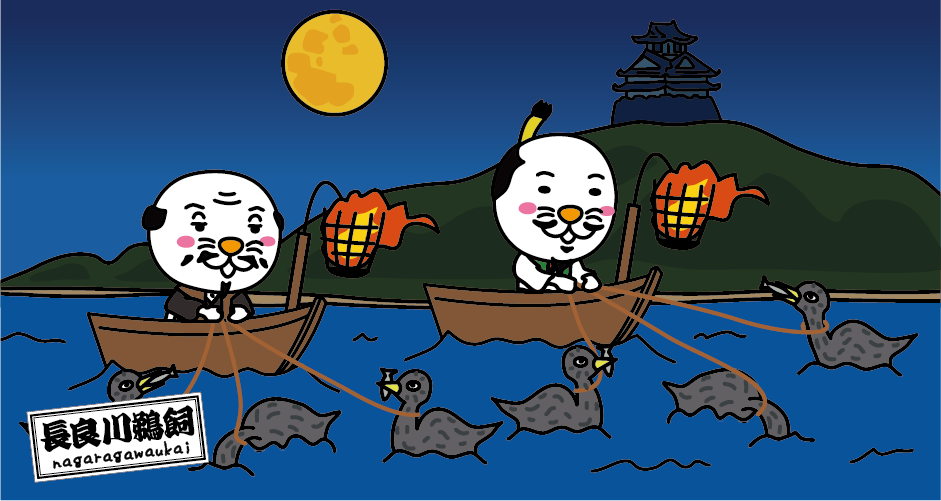
Cormorant fishing
I don’t know how the cormorants feel, but I think they probably enjoy catching fish. Rather, humans are more attentive so that the cormorants can catch fish comfortably.
Cormorant fishing is a traditional fishing method that uses trained cormorants to catch river fish such as sweetfish (ayu). Cormorant fishing is called “Ukai” in Japanese. Cormorant fishing has a long history, with clay figures depicting cormorant fishing excavated from ancient tombs in Gunma Prefecture dating back to the 5th and 6th centuries. Cormorant fishing is mentioned in Japan’s oldest history books, “Kojiki” and “Nihon Shoki”, and in the Chinese history book “Suishu (Book of Sui)” (7th century), cormorant fishing in Japan is recorded as the oldest in the world. Cormorant fishing has been practiced for over 1400 years. By the way, cormorant fishing is practiced only in Japan and China. The cormorants used in cormorant fishing are Sea Cormorants (Japanese Cormorants) in Japan and River Cormorants (Great Cormorants) in China. Sea Cormorants are larger and stronger than River Cormorants, and seem to have a more docile personality. It is said that the reason why Sea Cormorants are used in cormorant fishing in Japan is that instead of cormorant fishing in the shallow waters of the river, cormorant fishing in which the cormorants are manipulated from a boat became mainstream, and larger cormorant suitable for this were preferred.
(Cormorant fishing that takes place in the shallow waters of a river is called “KachiU, walking cormorant fishing.”)
<Cape Unomisaki>
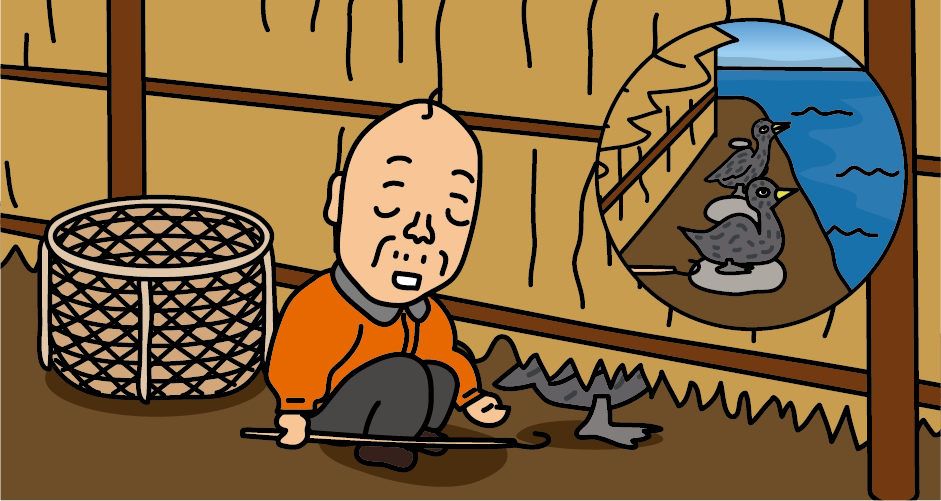

It is difficult for Sea Cormorants to breed in an artificial environment, so wild cormorants caught in the Cape Unomisaki, Ibaraki Prefecture, the only place in Japan where hunting is permitted, are trained for two or three years before being used for cormorant fishing.
<Cormorant fishermen, Usho>
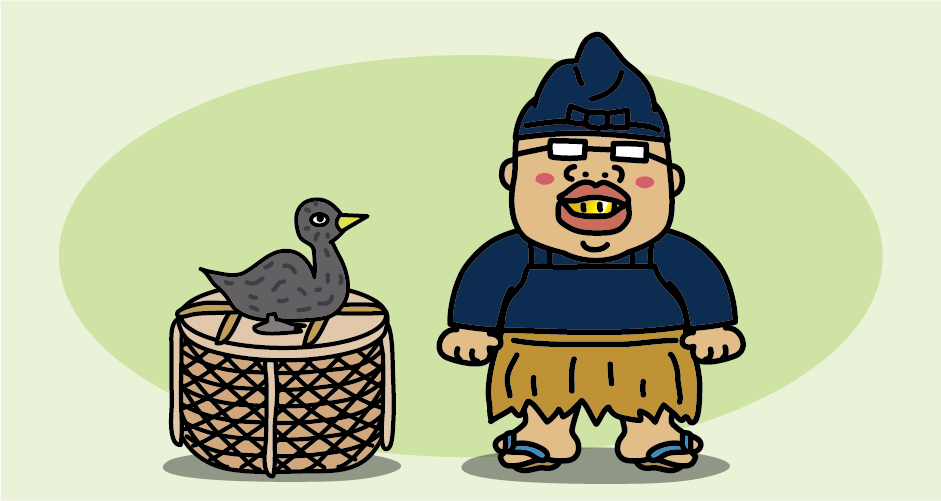

In cormorant fishing, the person who manipulates the cormorants is called “Usho, cormorant fisherman,” and it is said that Nobunaga Oda gave this name. Cormorant fishermen wear kazaori-Eboshi hat, fishing clothes, breastplates, Koshimino (grass skirts), and Ashinaka (half-soled straw sandals).
Fishing clothes are black or dark blue so as not to frighten the cormorants when fishing at night. Kazaori-Eboshi hat is a cloth wrapped around the head to protect the hair from the sparks of the bonfire, it got its name from the fact that the ends of the cloth look like it is being blown by the wind. A breastplate is a piece of cloth that used to protect the chest of an open fishing suit from sparks of bonfire. Koshimino is a type of traditional rain gear made of woven rice straw that covers the body from the waist down to protect it from splashing water. Ashinaka is a pair of sandals worn on the toes, which is half a regular straw sandal to prevent slipping on the wet floor of the ship.
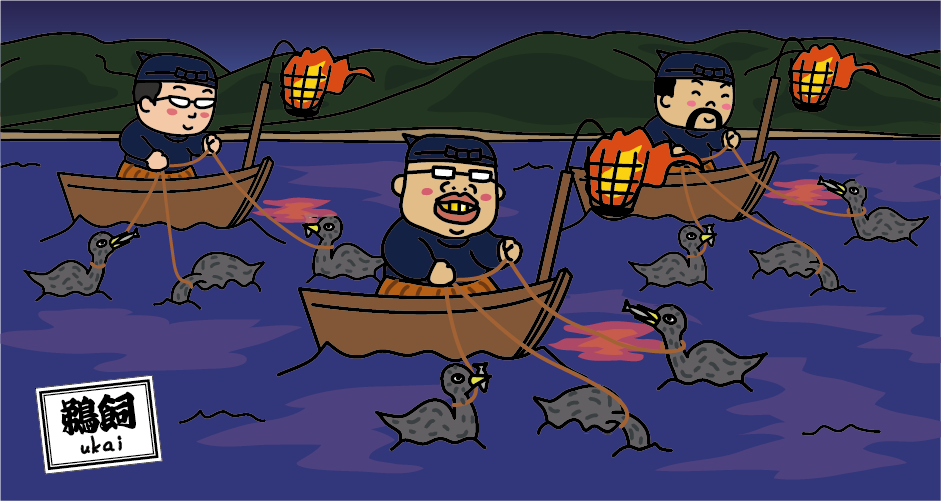
<Cormorant fishing boat, Ubune>
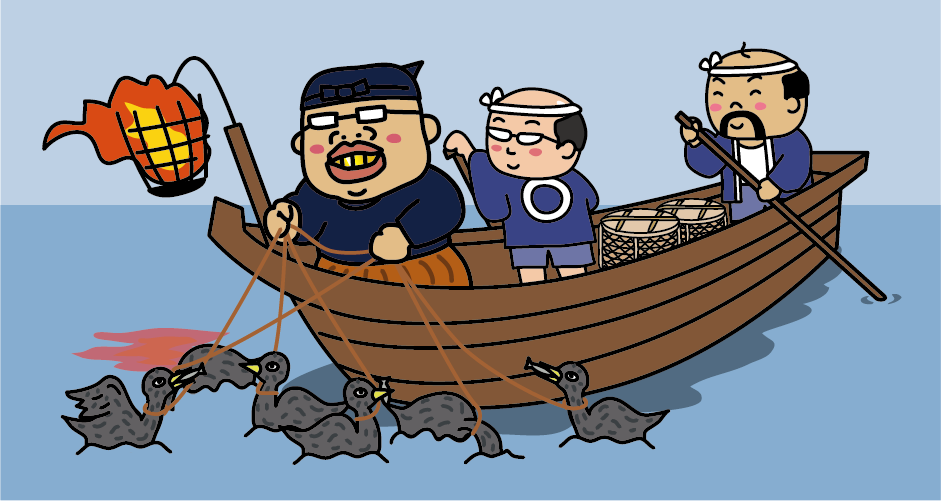

Boats used for cormorant fishing are called Ubune. Ubune is about 13 meters long, and consists of a group of three people, including the cormorant fisherman (Usho), a “tomonori”‘ who steers the boat, and a “nakanori” who is an assistant. Cormorants are related to pelicans, and cormorant fishing is a fishing method that uses the habit of cormorants to spit out the fish they have stored in their throats. A bonfire is attached to the bow of the boat, and the cormorants catch one after another the sweetfish that are startled by the light of the bonfire that shines on the surface of the river and become active. Each cormorant fisherman handles 6 to 12 cormorants.
<Walking Cormorant fishing, Kachi-u>
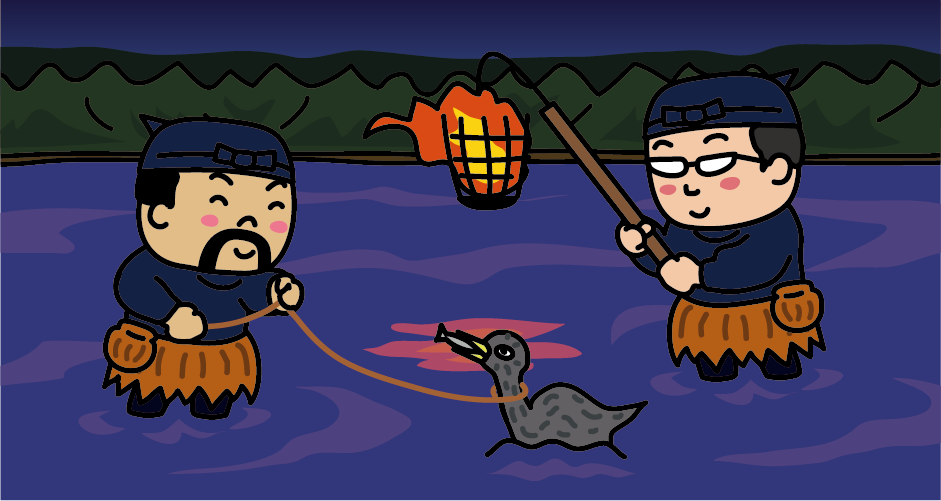

Cormorant fishing that does not use a cormorant fishing boat is called “Kachi-u (walking cormorant fishing).” While building a bonfire in the shallow waters of the river, the cormorant fishermen enter the river directly and fish with one or two cormorants.
<Uayu, Sweetfish with the mark of a cormorant’s beak>
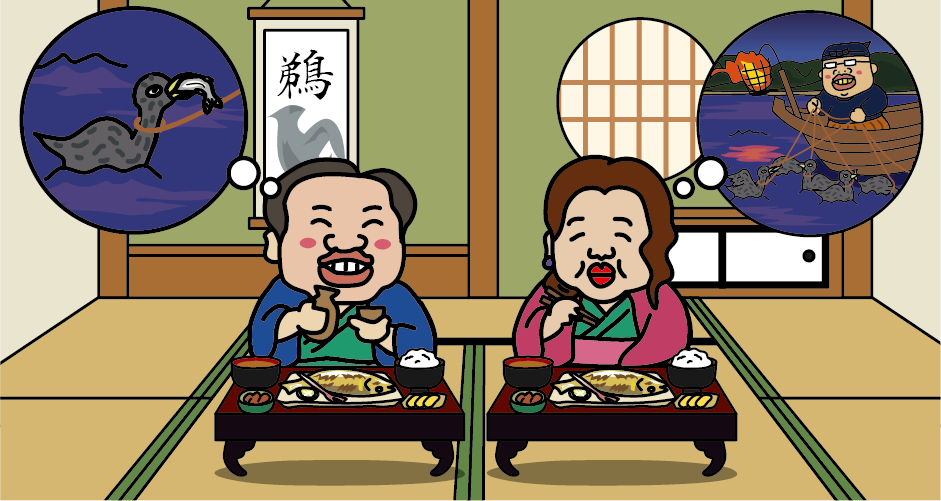

The sweetfish (ayu) caught by cormorant fishing are called “Uayu”, and they have marks from the beak of a cormorant. Uayu are popular because they are fresh and delicious because it kills sweetfish instantly with its beak, but Uayu are not sold in the market. It is said that Uayu are used as food for cormorants after cormorant fishing, and are sold to some inns and restaurants.
<cormorant fisher’s house>
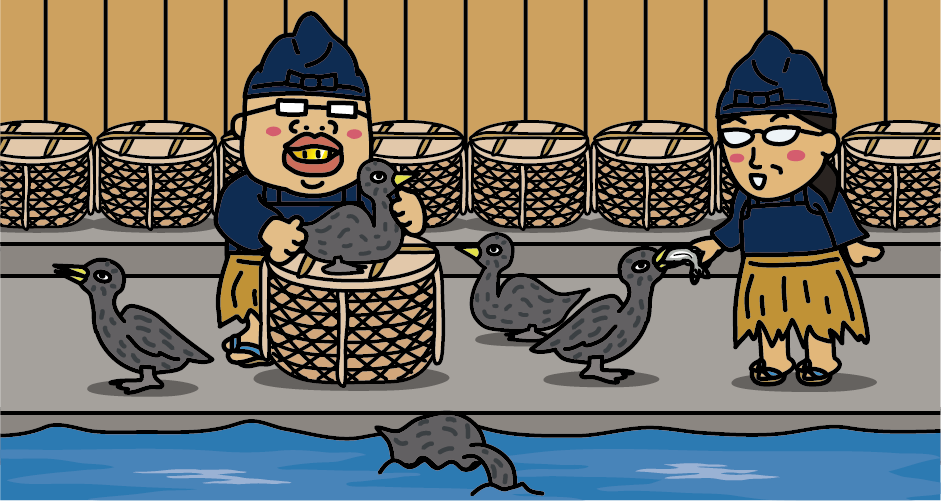

Cormorant fisherman and cormorants live together every day. For cormorant fishermen, cormorants are like family members. Cormorants who are old and unable to fish continue to live in the cormorant fisher’s house, so while wild cormorants live for 3 to 4 years, cormorants in cormorant fishing live about 15 years longer.
<Cormorant fishing: 11 places nationwide>
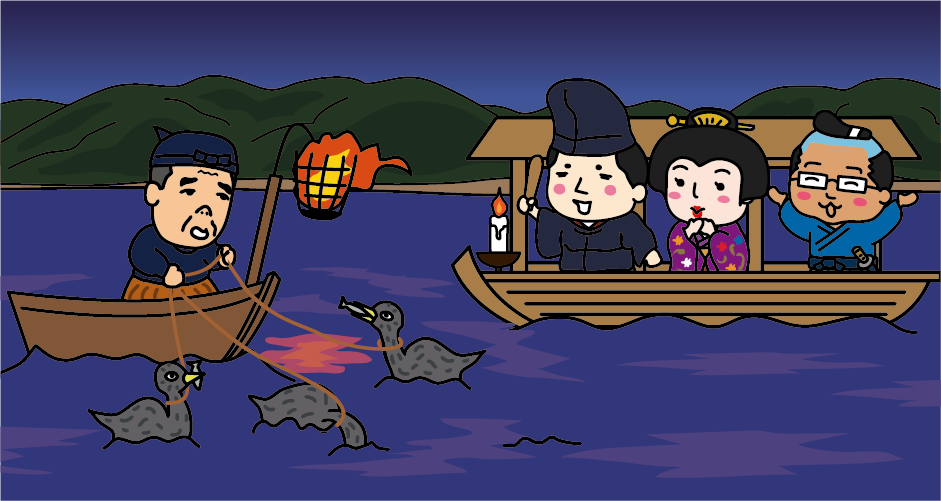

Since the Heian period (8th century), emperors, aristocrats, and samurai have watched cormorant fishing in Japan. Even today, cormorant fishing is still watched in various places, mainly in western Japan.
- “Isawa Ukai” (Waiking cormorant fishing) in Fuefuki City, Yamanashi Prefecture (Fuefuki River)
- “Nagaragawa Ukai” (imperial cormorant fishing) in Gifu City, Gifu Prefecture (Nagara River)
- “Oze Ukai” (imperial cormorant fishing) in Seki City, Gifu Prefecture (Nagara River)
- “Kisogawa Ukai” in Inuyama City, Aichi Prefecture (Kiso River)
- “Uji Ukai” in Uji City, Kyoto Prefecture (Uji River)
- “Arashiyama Ukai” in Kyoto City, Kyoto Prefecture (Oi River)
- “Miyoshi Ukai” in Miyoshi City, Hiroshima Prefecture (Basen River)
- “Kintaikyo Ukai ” in Iwakuni City, Yamaguchi Prefecture (Nishiki River)
- “Ozu Ukai” in Ozu City, Ehime Prefecture (Hiji River)
- “Mikumagawa Ukai” in Hita City, Oita Prefecture (Mikuma River)
- “Chikugogawa Ukai” in Asakura City, Fukuoka Prefecture (Chikugo River)












You need to login to comment on an article.